Waste management in our facilities
Some of our projects
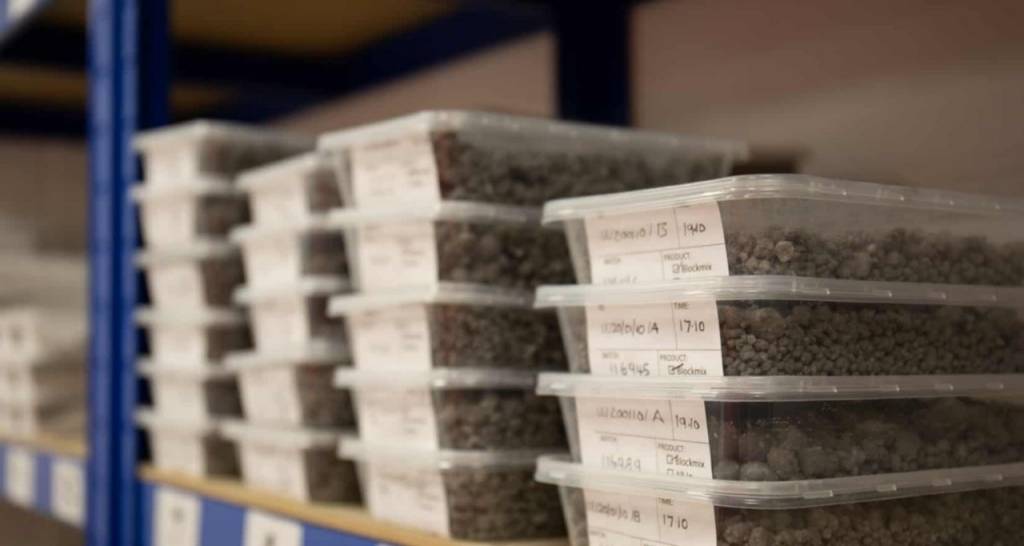
Soil bioremediation in Peru
The project is noteworthy for its pursuit of more environmentally-friendly alternatives like the possibility of treating soils that may contain hydrocarbons in a remote area. This is done through a process called on-site bioremediation instead of traditional treatment with the help of third parties, which would require the long-distance transportation of the waste.
At the facilities, we analyze and identify the possibility of treating these soils through an aerobic bioremediation technique that employs compost available at that same location obtained from organic food waste, which ends with the soils being deposited into an approved pit. Since 2019, we have treated more than 500 tonnes of soils.
Creating our own compost and seeking synergies with local communities
The majority of our exploration and production operations in remote areas generates a certain amount of organic waste that we convert into new resources for our activities or for the local community's use.
Composting improves the treatment of organic waste, which consists of a modification in the final disposal of organic waste that is derived from cooking. Through this, we are able to:
- Provide nutrients to the soil as a fertilizer for crops.
- Restore over-developed areas and carry out revegetation activities.
- Convert waste into a useful element for us and our surroundings.
Along with:
- More than 90 tonnes of compost have been generated since 2019 at our facilies in Block 57 in Perú, and the Margarita field in Bolivia. This compost was used to fertilize soil in our facilities and local communities.
- More than 400 tonnes of organic waste have been produced in the cafeterias at our facilities in Bolivia since 2019. This waste was donated to nearby cattle farms as animal feed.
Reusing water
In our exploration and production activities, we reuse water in many of our processes. With the aim of reducing our dependence on fresh water, we seek alternatives like:
- Reducing fresh waster consuption by reusing contaminated underground water to improve operational process efficiency in Canada
- Capturing and storing rain water to be used in construction projects on roads and pathways in our exploration projects in Bolivia
- Recovering desalinated brackish water to reduce the fresh water consumption of our operations in Venezuela

Classification by key lines and value chain
Our circular economy projects are aligned with the key lines of our strategy and are present throughout our entire value chain, from obtaining raw materials to commercializing products and services.